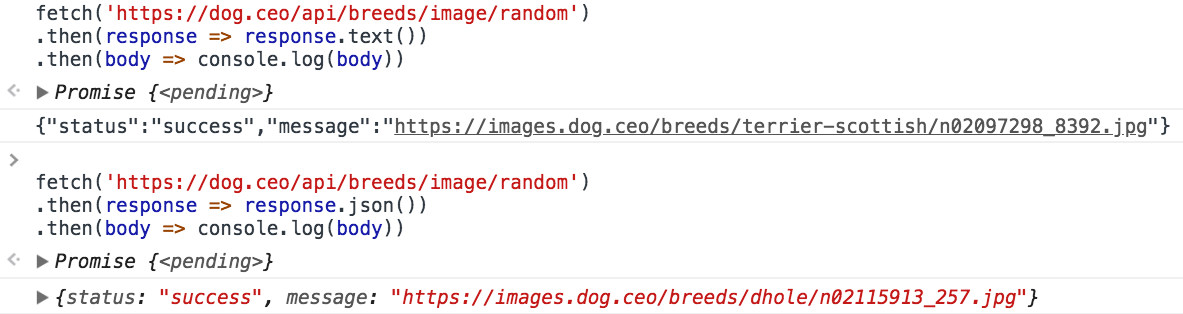
A response has a body, accessible using several methods:
text()returns the body as a stringjson()returns the body as a JSON-parsed objectblob()returns the body as a Blob objectformData()returns the body as a FormData objectarrayBuffer()returns the body as anArrayBufferobject
All those methods return a promise. Examples:
fetch('./file.json')
.then(response => response.text())
.then(body => console.log(body))
fetch('./file.json')
.then(response => response.json())
.then(body => console.log(body))
The same can be written using async functions
;(async () => {
const response = await fetch('./file.json')
const data = await response.json()
console.log(data)
})()
Lessons in this unit:
| 0: | Introduction |
| 1: | How to use Fetch |
| 2: | Catching errors in network requests |
| 3: | The Response object |
| 4: | ▶︎ Getting the body content |
| 5: | The Request object |
| 6: | Request headers |
| 7: | POST requests |