The DOM is a tree of elements, with the Document node at the root, which points to the html Element node, which in turn points to its child element nodes head and body, and so on.
From each of those elements, you can navigate the DOM structure and move to different nodes.
Getting the parent
Every element has just one parent.
To get it, you can use Node.parentNode or Node.parentElement (where Node means a node in the DOM).
They are almost the same, except when ran on the html element: parentNode returns the parent of the specified node in the DOM tree, while parentElement returns the DOM node’s parent Element, or null if the node either has no parent, or its parent isn’t a DOM Element.
People usually use parentNode.
Getting the children
To check if a Node has child nodes, use Node.hasChildNodes() which returns a boolean value.
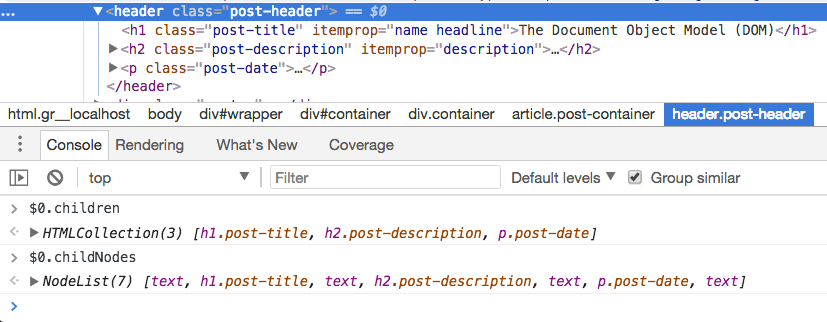
To access all the Children Element Nodes of a node, use Node.childNodes.
The DOM also exposes a Node.children method. However, it does not just include Element nodes, but also the white space between elements as Text nodes. This is not something you generally want.
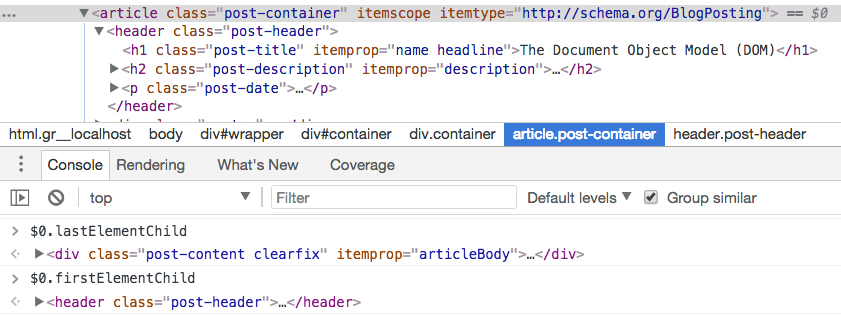
To get the first child Element Node, use Node.firstElementChild. To get the last child Element Node, use Node.lastElementChild:
The DOM also exposes Node.firstChild and Node.lastChild, with the difference that they do not “filter” the tree for Element nodes only. They will also show empty Text nodes that indicate white space.
In short, to navigate children Element Nodes use
Node.childNodesNode.firstElementChildNode.lastElementChild
Getting the siblings
In addition to getting the parent and the children, since the DOM is a tree you can also get the siblings of any Element Node.
You can do so using
Node.previousElementSiblingNode.nextElementSibling
The DOM also exposes previousSibling and nextSibling, but as their counterparts described above, they include white spaces as Text nodes, so you generally avoid them.
Lessons in this unit:
| 0: | Introduction |
| 1: | The `window` object |
| 2: | The `document` object |
| 3: | Types of nodes |
| 4: | ▶︎ Traversing the DOM |
| 5: | Editing the DOM |