Let’s see how a file can be added to Git. Type:
echo "Test" > README.txt
to create a file. The file is now in the directory, but Git was not told to add it to its index, as you can see what git status tells us:
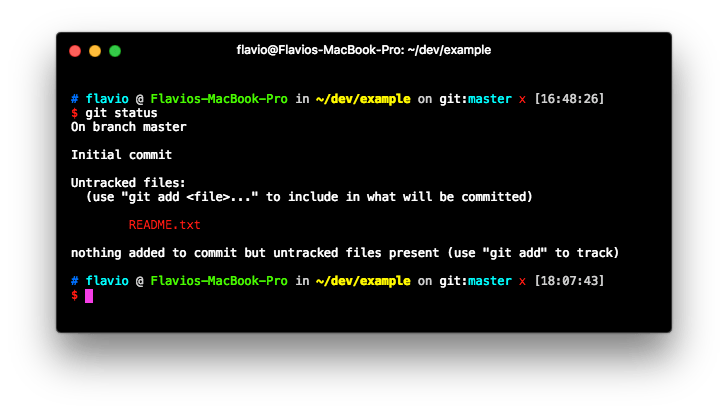
Now we need to add the file to the repository with:
git add README.txt
This commands add the file to the staging area:
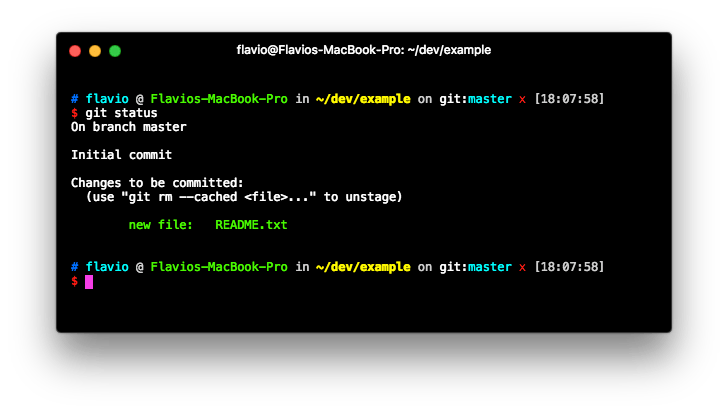
Once a file is in the staging area, you can remove it by typing:
git reset README.txt
But usually what you do once you add a file is commit it.
Once you have one or more changes to the staging area, you can commit them using
git commit -am "Description of the change"
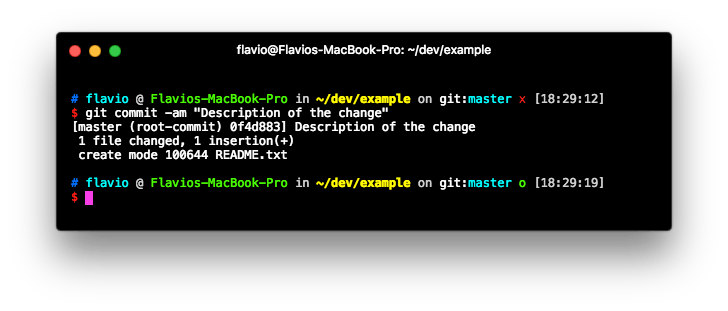
This cleans the status of the staging area:

and permanently stores the edit you made into a record store, which you can inspect by typing git log:
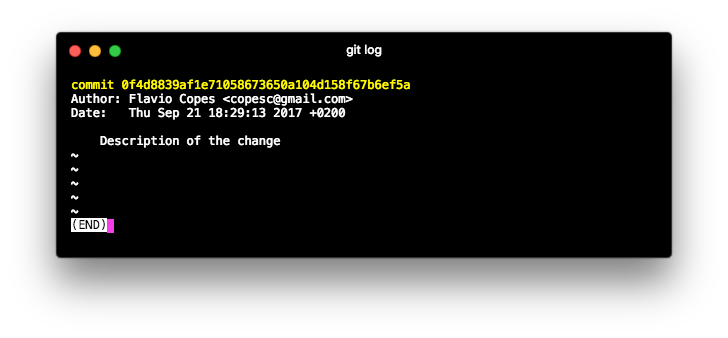
Lessons in this unit:
| 0: | Introduction |
| 1: | Installing Git |
| 2: | Initialize a repository |
| 3: | ▶︎ Commit changes |
| 4: | Branches |
| 5: | Push and pull |
| 6: | Working with a remote |
| 7: | Solving conflicts |
| 8: | .gitignore |